Understanding Reinforced Concrete Beams: Design, Construction, and Performance
- timotee47
- Sep 1, 2023
- 3 min read

Reinforced concrete beams are fundamental components in the construction industry, providing structural support in buildings, bridges, and a wide range of infrastructure projects. These beams are crucial for distributing loads and ensuring the stability and durability of structures. In this technical writing, we will delve into the world of reinforced concrete beams, exploring their design principles, construction methods, and performance considerations.
1. Reinforced Concrete Beam Design
1.1 Purpose of Reinforcement
Reinforced concrete beams consist of two primary materials: concrete and steel reinforcement. The concrete provides compressive strength, while the steel reinforcement, typically in the form of bars or mesh, adds tensile strength. The combination of these materials allows engineers to design beams capable of withstanding complex loading conditions.
1.2 Design Considerations
Designing reinforced concrete beams involves several critical considerations:
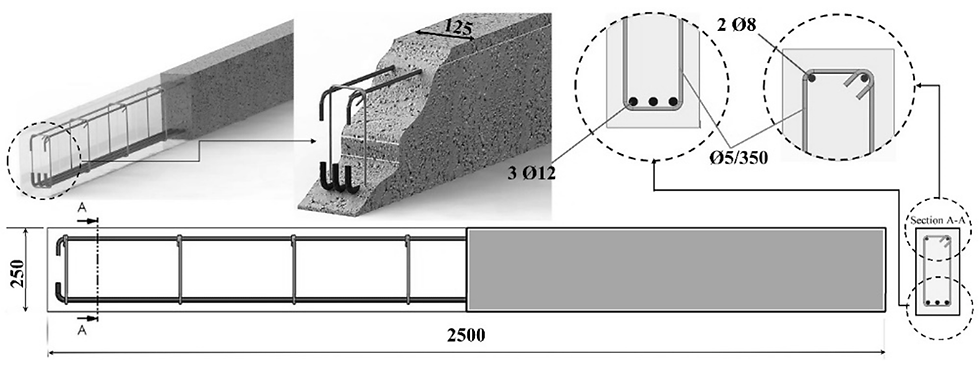
1.2.1 Load and Span
The type and magnitude of the loads a beam will carry influence its dimensions and reinforcement requirements. Engineers consider factors such as dead loads (permanent), live loads (variable), and environmental conditions.

1.2.2 Material Properties
The choice of concrete mix and steel reinforcement grade must align with the project's requirements. Engineers calculate the required strength based on factors like the structure's intended use, exposure to environmental conditions, and safety standards.
1.2.3 Beam Geometry
The beam's dimensions, including depth, width, and span length, play a pivotal role in its ability to support loads. Engineers use structural analysis to determine the optimal geometry for a given application.
1.3 Structural Analysis
Structural analysis involves evaluating the internal forces and stresses within a beam under various loading conditions. This process helps determine the optimal reinforcement layout and size to ensure the beam's structural integrity.
1.3.1 Bending Moments
Bending moments are critical considerations in beam design. Engineers use mathematical models to calculate the distribution of moments along the beam's length, aiding in the placement of reinforcement.
1.3.2 Shear Forces
Shear forces perpendicular to the beam's axis can cause structural failure. Engineers carefully design shear reinforcement, such as stirrups, to prevent these failures.
2. Construction of Reinforced Concrete Beams
2.1 Formwork
The construction of reinforced concrete beams begins with formwork. This temporary structure, often made of wood or metal, defines the beam's shape and holds the concrete in place until it cures. Proper formwork is essential for achieving the desired beam dimensions and finish.

2.2 Placing Reinforcement
Steel reinforcement bars or mesh are placed within the formwork according to the engineered design. This process involves securing the reinforcement to prevent displacement during concrete placement.
2.3 Concrete Placement
Once reinforcement is in place, concrete is poured into the formwork. The quality of concrete placement is critical to ensure the structural integrity of the beam. Proper compaction and consolidation are essential to eliminate air voids.
2.4 Curing
Curing is the process of maintaining adequate moisture and temperature conditions for the concrete to achieve its designed strength. Proper curing prevents cracking and enhances the durability of the beam.
3. Performance of Reinforced Concrete Beams
3.1 Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity
The performance of reinforced concrete beams is primarily evaluated based on their strength and load-bearing capacity. Engineers conduct various tests, such as flexural strength tests, to ensure that beams can safely carry the intended loads without failure.
3.2 Durability
Durability is a crucial aspect of beam performance, particularly in outdoor or aggressive environments. Concrete cover thickness and the quality of concrete and reinforcement materials play vital roles in ensuring long-term durability.
3.3 Deflection and Serviceability
Excessive deflection can affect the usability and aesthetics of a structure. Engineers calculate and monitor deflection to ensure it falls within acceptable limits.
3.4 Cracking
Cracking in reinforced concrete beams is a common concern. While some cracks may be superficial, others can compromise structural integrity. Engineers assess crack widths and patterns to determine their impact on performance.
4. Maintenance and Repair
Maintenance and repair of reinforced concrete beams are essential for prolonging their service life. Regular inspections can identify issues such as corrosion of reinforcement or the development of cracks. Timely repairs, including patching and rehabilitation, can extend the beams' functional life.
5. Conclusion
Reinforced concrete beams are indispensable components in the construction industry, providing strength, stability, and durability to structures of all types. A thorough understanding of the design principles, construction methods, and performance considerations is crucial for engineers, architects, and construction professionals to ensure the safety and longevity of reinforced concrete beams in various applications.
Successful beam design involves a delicate balance of materials, geometry, and structural analysis to meet project requirements. Proper construction practices, including formwork, reinforcement placement, concrete quality, and curing, are essential for achieving the desired beam performance.
Ongoing performance evaluation, including strength testing, durability assessments, and crack monitoring, ensures that reinforced concrete beams continue to meet safety and functionality standards throughout their service life.
In the ever-evolving field of construction, where innovative materials and technologies are continually being developed, the principles and practices of reinforced concrete beam design and construction remain foundational, providing the backbone of many iconic structures worldwide.




Comments